前言
为了加深对Launcher3的整体印象,记录在工作上所遇到和解决的关于Launcher3定制开发的一些知识点,并且归纳总结成本系列文章。同时,也能起到帮助他人解决一些关于Launcher3相关定制的需求开发。
- Android Launcher3定制开发之结构
- Android Launcher3定制开发之改造横向化
- Android Launcher3定制开发之创建小部件
- Android Launcher3定制开发之预置快捷方式
- Android Launcher3定制开发之去除搜索和开机引导
- Android Launcher3定制开发之修改快捷方式图标
- Android Launcher3定制开发之添加负一屏
布局和结构
Launcher3主要分为拖动层(DragLayer)、工作区(WorkSpace)、搜索目标栏(SearchDropTargetBar)、单元布局(CellLayout)、页面指示符(PageIndicator)、热门位置(Hotseat),具体布局可以见下图,一图胜前言。
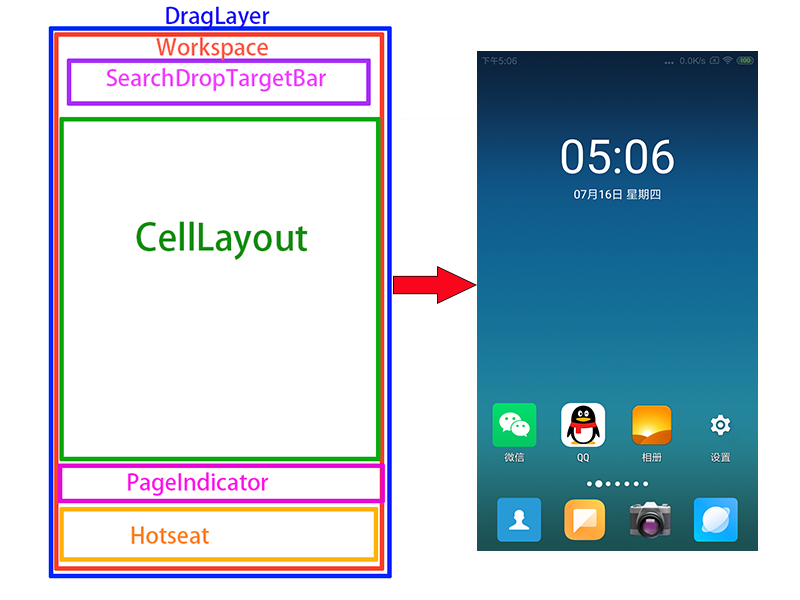
如图所示。最外层的是DragLayer层,可以从onTouchEvent中看出,它对AppWidgetResizeFrames做了传递判断,由此可见,它的作用是协调管理整个ViewGroup的拖动。WorkSpace作为DragLayer的子控件,它负责的是控制CellLayout的区域。换种说法就是,每一个CellLayout所包含的快捷图标、文件夹、小部件,都是由WorkSpace来处理和测量的。在它们之上,还有一个SearchDropTargetView的控件,该控件就是在用户长按快捷方式拖拽时所显示的View,当然,可以继承它去改造成符合业务的View来替换显示。
在整个ViewGroup层级中,所占比例最大的是CellLayout,它是桌面页面的基本单元,快捷图标、文件夹、小部件都是显示在它之上的,并且交给WorkSpace测量控制区域大小。滑动桌面,实际上就是多个CellLayout之间的切换。而为了显示CellLayout的切换,就有了中间的指示点,它叫做PageIndicator。另外为了符合更加人性化,提供常驻快捷方式位置栏,也就是Hotseat,它一般放置短信,拨号等最常用的应用,也可以定制化其他快捷方式,用户左右滑动屏幕时,该控件不做滑动处理。
数据加载过程
下面我们来说说,Launcher的应用数据是从何而来的。
在初始化Launcher的时候,可以看到首先是通过SharedPreferences和IconCache检测Launcher是否有Cache数据,然后初始化StateTransitionAnimation动画总线,之后再通过AppWidgetManager加载小部件。见代码所示:
mDeviceProfile = getResources().getConfiguration().orientation
== Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE ?
app.getInvariantDeviceProfile().landscapeProfile
: app.getInvariantDeviceProfile().portraitProfile;
mSharedPrefs = getSharedPreferences(LauncherAppState.getSharedPreferencesKey(),
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
mIsSafeModeEnabled = getPackageManager().isSafeMode();
mModel = app.setLauncher(this);
mIconCache = app.getIconCache();
mDragController = new DragController(this);
mInflater = getLayoutInflater();
mStateTransitionAnimation = new LauncherStateTransitionAnimation(this);
mStats = new Stats(this);
mAppWidgetManager = AppWidgetManagerCompat.getInstance(this);
mAppWidgetHost = new LauncherAppWidgetHost(this, APPWIDGET_HOST_ID);
mAppWidgetHost.startListening();
之后,通过检查离开桌面,来判断同步还是异步执行LauncherModel.startLoader()加载所有快捷方式。
if (!mRestoring) {
if (DISABLE_SYNCHRONOUS_BINDING_CURRENT_PAGE) {
mModel.startLoader(PagedView.INVALID_RESTORE_PAGE);
} else {
mModel.startLoader(mWorkspace.getRestorePage());
}
}
下面着重讲一下LauncherModel是如何加载所有快捷方式的。
LauncherModel.startLoader执行,实际上就是调用了LoaderTask.Run。在线程中,主要是做了两件事。一,加载workspace。二,加载所有app应用数据。
keep_running: {
loadAndBindWorkspace();
if (mStopped) {
break keep_running;
}
waitForIdle();
loadAndBindAllApps();
}
其中,loadAndBindWorkspace调用了loadWorkspaceScreensDb,最后读取workspaceScreens资源目录加载出来的。
ArrayList<Long> workspaceScreens = loadWorkspaceScreensDb(context);
synchronized(sBgLock) {
for (ItemInfo item : workspaceApps) {
if (item instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
// Short-circuit this logic if the icon exists somewhere on the workspace
if (shortcutExists(context, item.getIntent(), item.user)) {
continue;
}
}
}
....
}
public static ArrayList<Long> loadWorkspaceScreensDb(Context context) {
final ContentResolver contentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
final Uri screensUri = LauncherSettings.WorkspaceScreens.CONTENT_URI;
// Get screens ordered by rank.
final Cursor sc = contentResolver.query(screensUri, null, null, null,
LauncherSettings.WorkspaceScreens.SCREEN_RANK);
ArrayList<Long> screenIds = new ArrayList<Long>();
try {
final int idIndex = sc.getColumnIndexOrThrow(LauncherSettings.WorkspaceScreens._ID);
while (sc.moveToNext()) {
try {
long screenId = sc.getLong(idIndex);
screenIds.add(screenId);
} catch (Exception e) {
Launcher.addDumpLog(TAG, "Desktop items loading interrupted"
+ " - invalid screens: " + e, true);
}
}
} finally {
sc.close();
}
return screenIds;
}
而loadAndBindAllApps则是调用了LauncherAppsCompat.getActivityList读取系统桌面上的快捷方式并和本地Cache进行数据比对覆写。
final List<LauncherActivityInfoCompat> apps = mLauncherApps.getActivityList(null, user);
for (int i = 0; i < apps.size(); i++) {
LauncherActivityInfoCompat app = apps.get(i);
mBgAllAppsList.add(new AppInfo(mContext, app, user, mIconCache));
}
...
if (Utilities.ATLEAST_LOLLIPOP) {
sInstance = new LauncherAppsCompatVL(context.getApplicationContext());
} else {
sInstance = new LauncherAppsCompatV16(context.getApplicationContext());
}
...
public List<LauncherActivityInfoCompat> getActivityList(String packageName,
UserHandleCompat user) {
final Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
mainIntent.setPackage(packageName);
List<ResolveInfo> infos = mPm.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent, 0);
List<LauncherActivityInfoCompat> list =
new ArrayList<LauncherActivityInfoCompat>(infos.size());
for (ResolveInfo info : infos) {
list.add(new LauncherActivityInfoCompatV16(mContext, info));
}
return list;
}
最后,通过LauncherModel.updateWorkspaceScreenOrder更新Workspace以刷新桌面数据。
结语
本系列文章相关代码,可以通过点击这里找到。希望对大家学习和了解Launcher开发有所帮助。